
As most of you know, Google uses ranking systems that work with a number of algorithms to optimize the search results on the web and more than 200 signal affects the ranking criteria. As an exciting development, Google announced that it will use the web page experience as a ranking signal in May 2021, with a tweet it shared on November 10, 2020.
Evolution of the page experience
With this exciting news, the importance of user experience, which is one of the most popular trends recently, has been emphasized once again. Through the upcoming update, as well as providing the correct / searched result to users, Google will also take into account the user experience of the relevant web page. They will rank pages in organic results by taking into account negative metrics such as irrelevant and too many ads, page scrolling to gain more clicks and profits, and unsafe links.
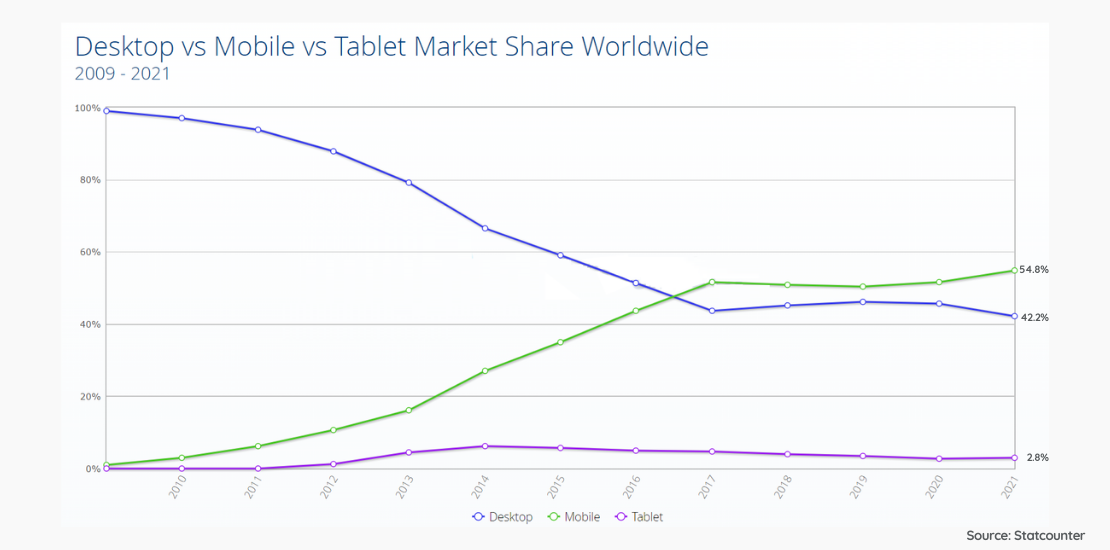
Especially in the last 5 years, with the use of mobile web leaving behind desktop web usage, the page experience offered more importance. In order to provide the user with the highest performance, it has become essential to measure the quality of the experience and to take action in this regard.
Before the Core Web Vitals update, the following metrics were used to rank the page experience:
- Compatibility with mobile devices
- Secure connection with HTTPs
- Safe browsing
- Accessible content (non-intrusive page, annoying popup, etc.)
In addition to the items above, the following new metrics have been added to specifically focus on the page experience:
- Page load time
- Page interaction time
- Visual stability
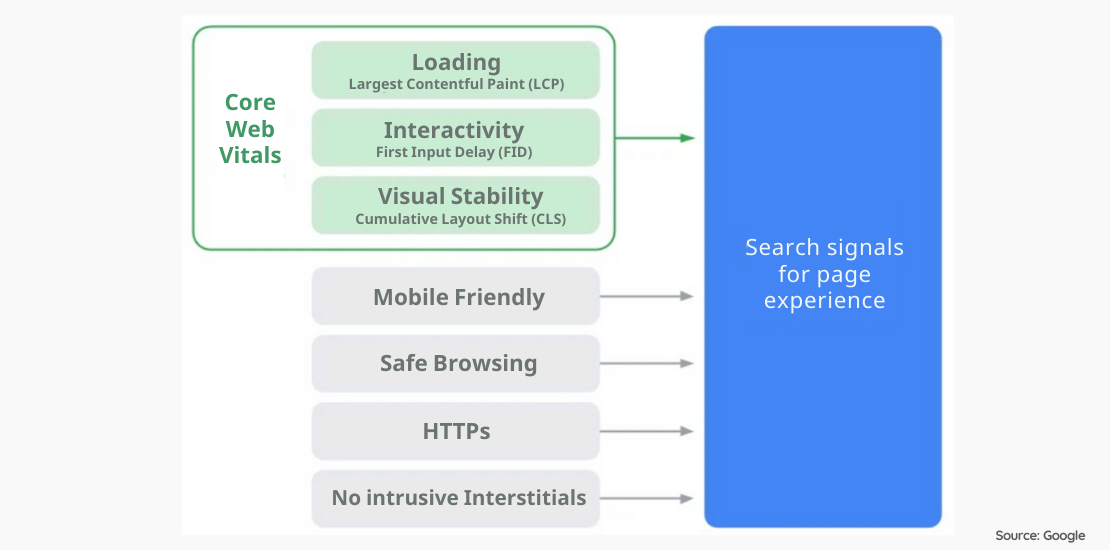
What are the components of Core Web Vitals?
Google specified the following three metrics as the Core Web Vitals:
Largest Contentful Paint: Refers to the time taken to load the main content of a web page (loading phase).
First Input Delay: The time it takes for a web page to be able to accept interaction (scroll, click, etc) (interactivity phase).
Cumulative Layout Shift: Indicates the amount of shift of the layout on the relevant page after the content becomes interactive (view phase).
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
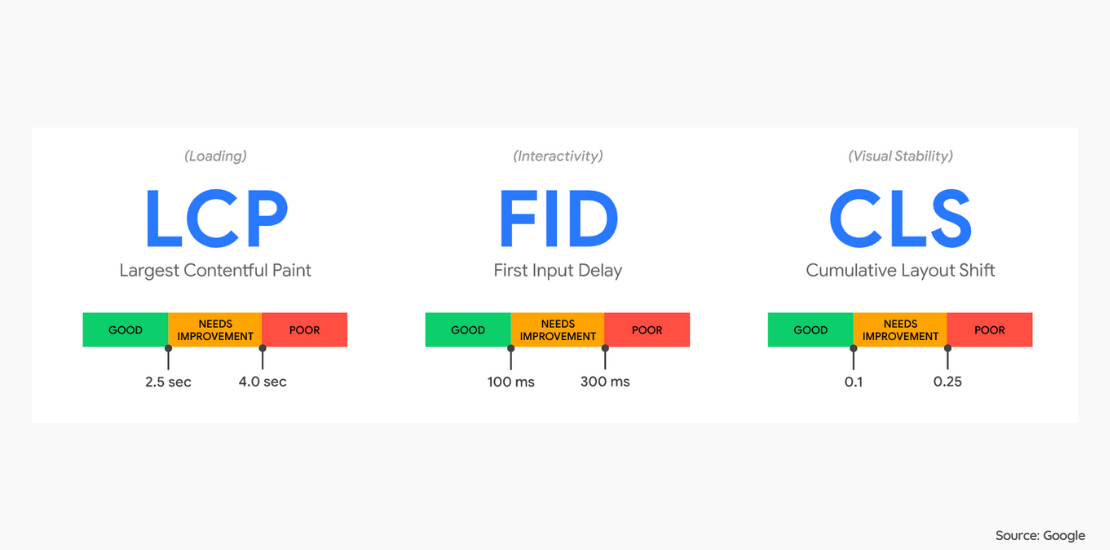
LCP refers to the loading of the largest (visible by user) element when loading a web page. The main purpose of LCP is to meet the perception and expectation that the page has been loaded by the users who want to visit the page. It is recommended to create the LCP within 2.5 seconds of the page starting to load.
For more LCP optimization suggestions you can check the official Google document regarding this topic.
First Input Delay (FID)
FID refers to the response time given to the action taken by the user. A late response to actions taken by the user who provides access to the page such as scrolling or clicking may create the impression that “the scroll function is not working” or that “the button is broken”, thus “there is something wrong with this page”. According to Google, the response time for FID should be 100ms or less. Results above of this value require improvement. Google suggests several ways to optimize the FID.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
CLS is the metric that expresses the shift of the relevant page after the web page is opened.
The CLS metric was created specifically to relegate the websites which ignore the user experience in order to increase revenue from clicks in organic search results. The CLS assigns a score to each unexpected layout shift on the page, measuring their sum and determining a value accordingly. This value is expected to be 0.1.
The aim is to define the places of the elements on the page as fixed and to prevent unexpected shifts. As an important topic, there are several steps to decrease CLS.
What should be the ideal LCP, FID, and CLS values according to Google?

How to check the performance of Core Web Vitals?
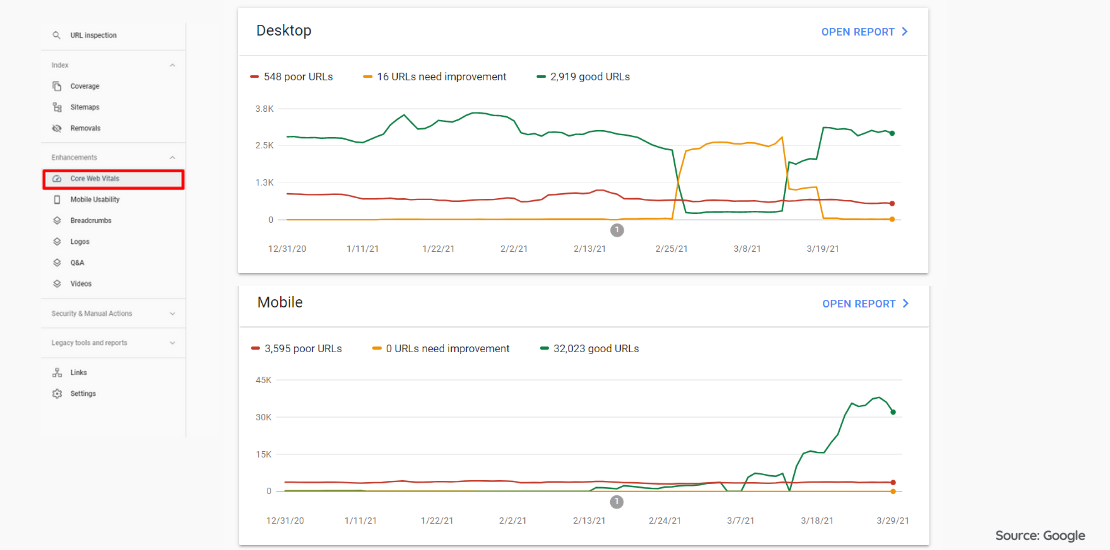
Google’s site speed tool provides the way of scoring CWV metrics and the metrics that need to be optimized.
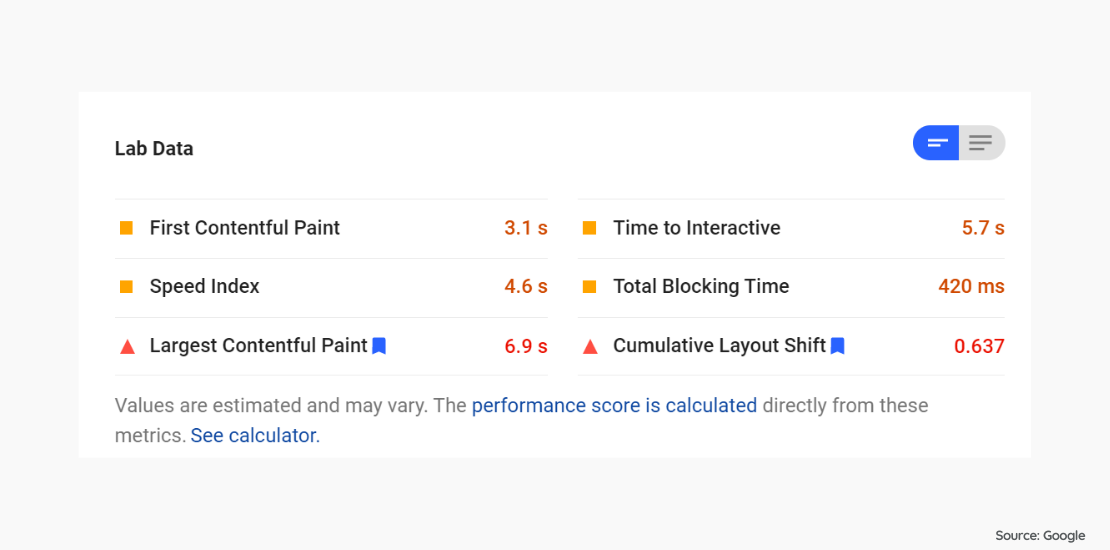
While the related report generates the results for a single web page, you can obtain the results of multiple pages for mobile and desktop websites in the Core Web Vitals report under the Google Search Console> Enhancements tab.
What will be the next steps after the Core Web Vitals update?
Google put Mobile-First Indexing to the center by taking the priority of the website crawling from the desktop and making mobile site browsing a priority. The main motivation for putting this application into practice is that the majority of the users are on mobile now. In other words, user behavior shaped and evolved Google’s strategies. When we consider all these developments, we see that the ranking signals considered by Google will be more in the focus of user experience.

The metrics we mentioned above such as LCP, FID, CLS are important to increase the quality of user experience and to create an easily navigable and actionable web world. While developing websites both in terms of content and technique, the starting point should be “being user friendly” and improvements should be implemented from this point of view. Applying the metrics developed to create user-friendly journeys and presenting the journey that gives the best results with A / B tests is the essential point to be successful.
The SEO team performing under the Inveon GrowthLab team takes the necessary actions to identify existing Core Web Vitals problems and send them to the development team with their solution suggestions to start the user experience optimization process. After the necessary technical improvements are made, the result of the work is reported by asking Google to verify that the error has been corrected. As a result of these processes, your website is ensured to create the highest level of user experience, and thus your e-commerce operations can progress with high performance.
Get in touch with Inveon GrowthLab today to keep up with the renewed trends and ensure the success of your brand.

